Answer 1 of 15. But before I get to the physics.
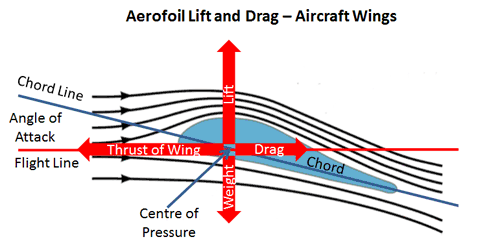
Aerodynamic Lift And Drag And The Theory Of Flight
Because the upper flow is faster then from Bernoullis equation the pressure is lower.

How a wing creates lift. The wing area is defined as the top view area of the wing when looking down on the aircraft from above or below. You can mount two or more wings on a central shaft and. A wing flying through air reduces the air pressure above the wing a.
The popular explanation of lift. HOW A WING WORKS. How do airplane wings produce lift.
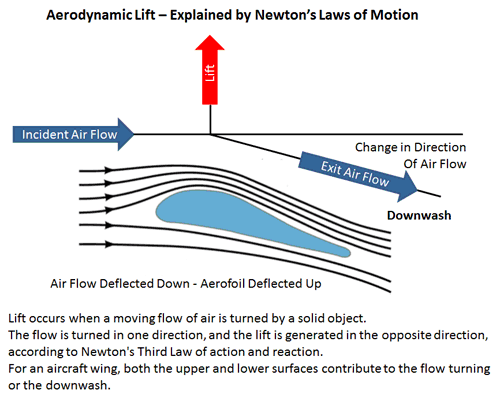
Aerodynamics - why wings create lift - current vs historical discussions. This week Im talking to Olympic Sailor Hunter Lowden. Both the upper and lower surfaces of the wing act to deflect the air.
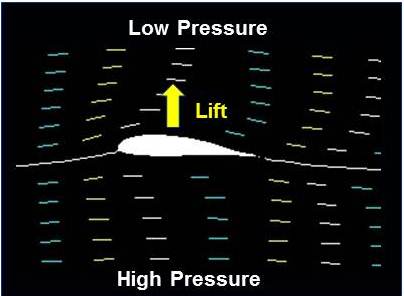
The wings provide lift by creating a situation where the pressure above the wing is lower than the pressure below the wing. There is a net change of momentum in the vertical plane between the leading and trailing edges of the airfoil and by necessity of Newtons third law this creates a lift force. A simple sink top aspirator creates a strong vacuum.
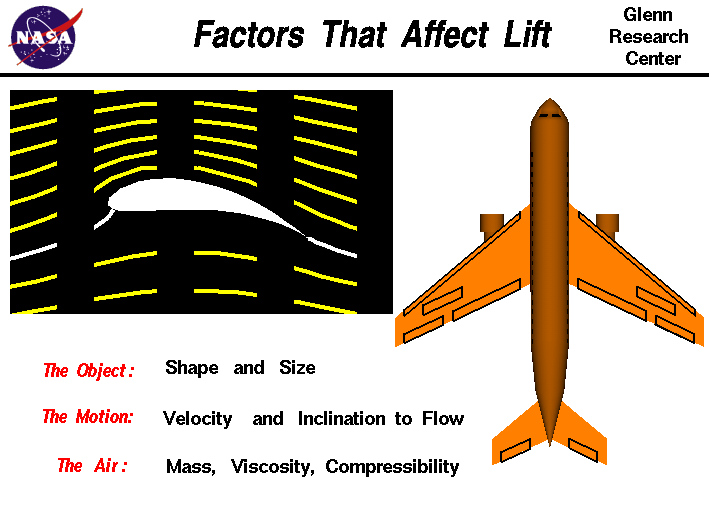
From intuition it can be thought of that a larger wing area will create a larger lift. This has been covered many times some good some ok and many wrong. This is the area that is normal or perpendicular to the lift force that is generated.
Lift force is also created by airstream striking an angled surface bottom of wing. If you can understand how a sail works as well as a wing on an airplane youll be in a small minority of people who truly understand the basic aerodynamic theory. The faster the air travels the lower the static air pressure becomes.
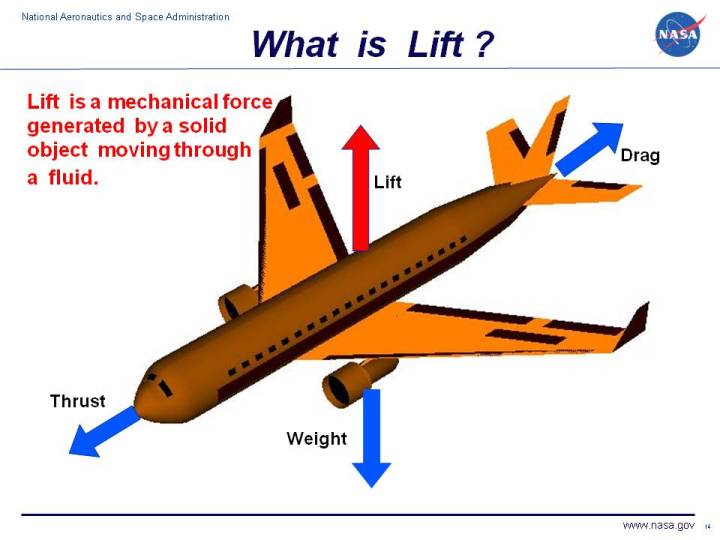
Since the pressure below the wing is higher than the pressure above the wing there is a net force upwards. Lift is an important concept not only in flying but also in sailing. The wings of an aircraft are airfoils designed to create this force of vertical motion.
According to this explanation the slight downward deflection of the air leaving the trailing edge of a wing is what produces lift. The amount of lift depends on the speed of the air around the wing and the density of the air. A wing moving through air creates pressure differences because it has to push the air around to get thr.
A rotary motion is the easiest way to keep a wing continuously moving. Any surface that alters the airflow to the advantage of a produced force in a particular direction is termed as an airfoil. Merged with How do wings create a lift force.
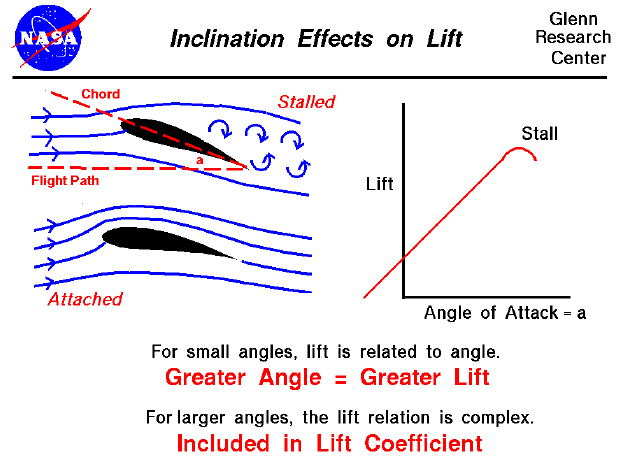
Its often said that this happens because the airflow moving over the top curved surface has a. Flying at an angle of attack changes where the division of the top and bottom air occurs near the leading edge of the wing. The main goal of a wing is to create a force that is equal to the weight of the aircraft but pointing in the opposite direction so the thrust of the wing can lift the aircrafts weight.
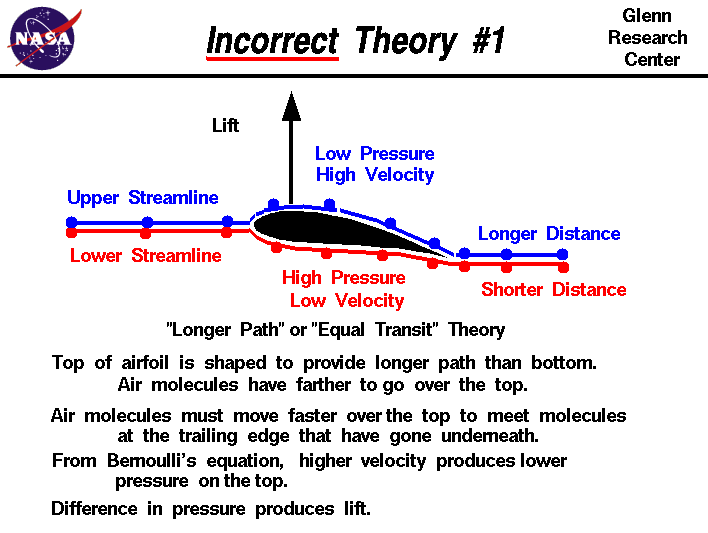
Since for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction the downward push on the air must result in an upward push on the wing. Now University of Cambridges Professor Holger Babinsky has created a 1-minute video that he hopes will finally lay to rest a commonly used yet misleading explanation of how wings lift. Students of physics and aerodynamics are taught that airplanes fly as a result of Bernoullis principle which says that if air speeds up the pressure is lowered.
To create this pressure difference the surface of the wing must satisfy one or both of the following conditions. There is more than one source of lift. As I mentioned before sails on a sailboat are similar to wings on an airplane.
In order to meet up at the trailing edge the molecules going over the top of the wing must travel faster than the molecules moving under the wing. A wing lifts when the air pressure above it is lowered. So the fast air on top and the slow air on bottom creates a pressure differential across the wing creating lift.
Another explanation that is often cited for explaining lift is that the airfoil pushes air downwards ie. Now University of Cambridges Professor Holger Babinsky has created a 1-minute video that he hopes will finally lay to rest a commonly used yet misleading explanation of how wings lift. The net downward motion of the air is an action for which the equal and opposite reaction is a lift force on the wing.
But this downwash results from air pressure differences on the wingit. How airfoil wings generate lift2. The difference in pressure across the airfoil produces the lift.
A wings trailing edge must be sharp and it must be aimed diagonally downwards to create lift. The curved shape of a wing creates an area of low pressure up above it red which generates lift. Wings create lift by deflecting air downward and benefiting from the equal and opposite reaction that results see How Airplanes Work for details -- the article contains a complete explanation of how wings produce lift.
Feb 26 2020 19 russ_watters. Probably the most common examples of how aerodynamics works is with wings on an airplane. I continue to try to understand which one is most EFFICIENT.
Airplane wings designed as airfoils achieve this by interacting. The low pressure makes air accelerate over the wing and the curved shape of the wing and the higher air pressure well above the altered air stream forces that air into a powerful downwash also pushing the. Thus a wing generates lift because the air goes faster over the top creating a region of low pressure and thus lift.
How Does An Airplane Wing Create Lift By Deflecting Air Downward Quora

How Do Wings Generate Lift Aviation Stack Exchange
Aerodynamic Lift And Drag And The Theory Of Flight

How Does A Kite Fly Why The Kitesurf Fly Plane Ing And Kite

How Wings Actually Create Lift Youtube

How Planes Work The Science Of Flight Explain That Stuff

Aerodynamic Lift And Drag And The Theory Of Flight

How Do Wings Generate Lift Aviation Stack Exchange

Aerodynamics The Theory Of Lift Owlcation



Post a Comment
Post a Comment